
[ad_1]
Say howdy to ionocaloric cooling. It’s a brand new method to decrease temperatures with the potential to switch present strategies of chilling issues with a course of that’s safer and higher for the planet.
Typical refrigeration methods transport warmth away from an area by way of a gasoline that cools because it expands a long way away. As efficient as this course of is, a few of the selection gases we use are significantly unfriendly to the setting.
There is, nonetheless, a couple of means a substance might be pressured to soak up and shed warmth power.
A technique developed by researchers from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the University of California, Berkeley, within the US takes benefit of the best way that power is saved or launched when a cloth modifications part, as when strong ice turns to liquid water, for instance.
Raise the temperature on a block of ice, it’s going to soften. What we would not see so simply is that melting absorbs warmth from its environment, successfully cooling it.
One method to pressure ice to soften while not having to show up the warmth is so as to add a number of charged particles, or ions. Putting salt on roads to stop ice from forming is a standard instance of this in motion. The ionocaloric cycle additionally makes use of salt to vary a fluid’s part and funky its environment.
“The landscape of refrigerants is an unsolved problem,” mentioned mechanical engineer Drew Lilley from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in California in January 2023 assertion. “No one has successfully developed an alternative solution that makes stuff cold, works efficiently, is safe, and doesn’t hurt the environment.”
“We think the ionocaloric cycle has the potential to meet all those goals if realized appropriately.”
The researchers modeled the idea of the ionocaloric cycle to indicate the way it might doubtlessly compete with, and even enhance upon, the effectivity of refrigerants in use as we speak. A present operating via the system would transfer the ions in it, shifting the fabric’s melting level to vary temperature.
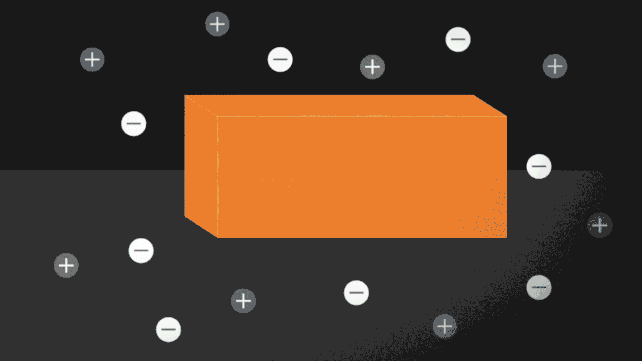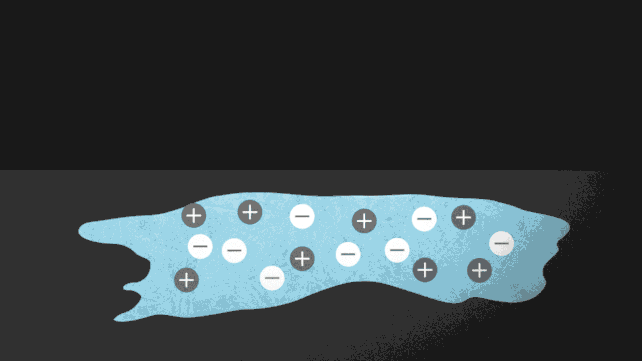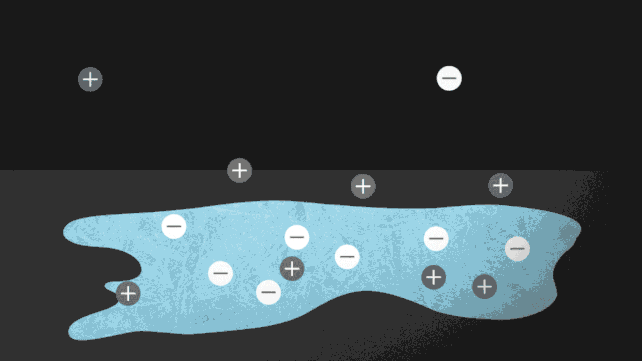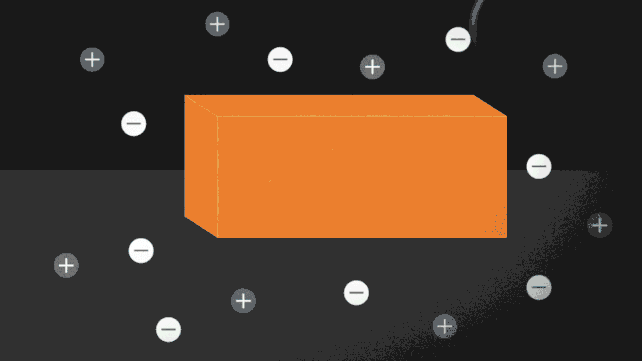
The workforce additionally ran experiments utilizing a salt made with iodine and sodium to soften ethylene carbonate. This frequent natural solvent can also be utilized in lithium-ion batteries and is produced utilizing carbon dioxide as an enter. That might make the system not simply GWP [global warming potential] zero however GWP adverse.
A temperature shift of 25 levels Celsius (45 levels Fahrenheit) was measured via the appliance of lower than a single volt of cost within the experiment, a end result that exceeds what different caloric applied sciences have managed to attain to this point.
“There are three things we’re trying to balance: the GWP of the refrigerant, energy efficiency, and the cost of the equipment itself,” mentioned mechanical engineer Ravi Prasher from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
“From the first try, our data looks very promising on all three of these aspects.”
The vapor compression methods at the moment utilized in refrigeration processes depend on gases which have excessive GWP, corresponding to numerous hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). Countries that signed as much as the Kigali Amendment have dedicated to lowering the manufacturing and consumption of HFCs by no less than 80 p.c over the subsequent 25 years – and ionocaloric cooling might play a significant half in that.
Now, the researchers have to get the expertise out of the lab and into sensible methods that can be utilized commercially and that scale up with none points. Eventually, these methods could possibly be used for heating in addition to cooling.
“We have this brand-new thermodynamic cycle and framework that brings together elements from different fields, and we’ve shown that it can work,” mentioned Prasher.
“Now, it’s time for experimentation to test different combinations of materials and techniques to meet the engineering challenges.”
The analysis was revealed in Science.
A model of this text was first revealed in January 2023.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink